Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Presentation
- Create a gMSA
- create the gMSA account
- Add the gMSA to the server
- Configure The services
The use of gMSA is an excellent way to properly secure your AD.
Generally it is too often accounts of services concerned by forgotten passwords, shares in YOLO mode 🤘 to all the group of admins of the planet, with obviously big privileges, little segmentation and a change of password every 10 years😬
Remember that just because you use gMSA doesn’t mean you can stop being vigilant about AD perms: If one can compromise an account with rights to the servers OU, or delegated administrative rights via GPO restricted groups or similar, or have the ability to modify a GPO that is linked to that OU, one can get administrative rights to the server.(Mimikatz against gMSA)
Presentation
- The same gMSA can be used on several servers
- gMSAs are stored in the “Managed Service Account” container in the Active Directory
- A gMSA can only be used on Windows Server 2012 and later
- Requires the use of Microsoft Key Distribution Service (kdssvc.dll) for automatic password management and account creation
- a gMSA is similar to a security group in which we will associate computer objects that will be allowed to use this secure service account
- The password is managed by the Active Directory, it is very very complex and nobody knows it
With an MSA or gMSA account, the password management is automatic by the Active Directory itself, unlike the use of a classic user account, which can be used for a service but for which you must manage the password renewal yourself. Very often, as it is time-consuming, the passwords of these accounts are not renewed by the admins 😭 . That’s why it’s useful to rely on the gMSA solution, which also offers increased security for credentials.🏆🏆🏆
An MSA account can be associated to only one server, unlike gMSA, which is restrictive when you need to use a service account on a service that is redundant between several servers.
In terms of compatibility, gMSA accounts work with different types of applications and features, including:
- Windows services
- Scheduled tasks
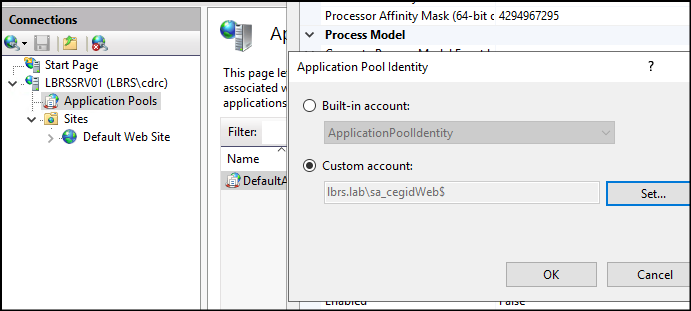
- IIS servers (Application Pool), SQL Server, ADFS, etc.
Create a gMSA
To be able to create gMSA accounts on Active Directory infrastructure, the Key Distribution Service must be running and a root key must be generated. To create a key from the domain controller, we will use PowerShell and the Add-KdsRootKey cmdlet.
It is possible to delay the activation of the generated key by using the -EffectiveTime parameter followed by a date. If we use the -EffectiveImmediately parameter the key will be usable 10 hours after its creation (default behavior) in order to ensure that it is replicated between the different DCs.
Here is the command to execute:
Add-KdsRootKey -EffectiveImmediately
As part of a lab, if you want to be able to use the KDS key now without having to wait 10 hours, it is possible to cheat by using this command:
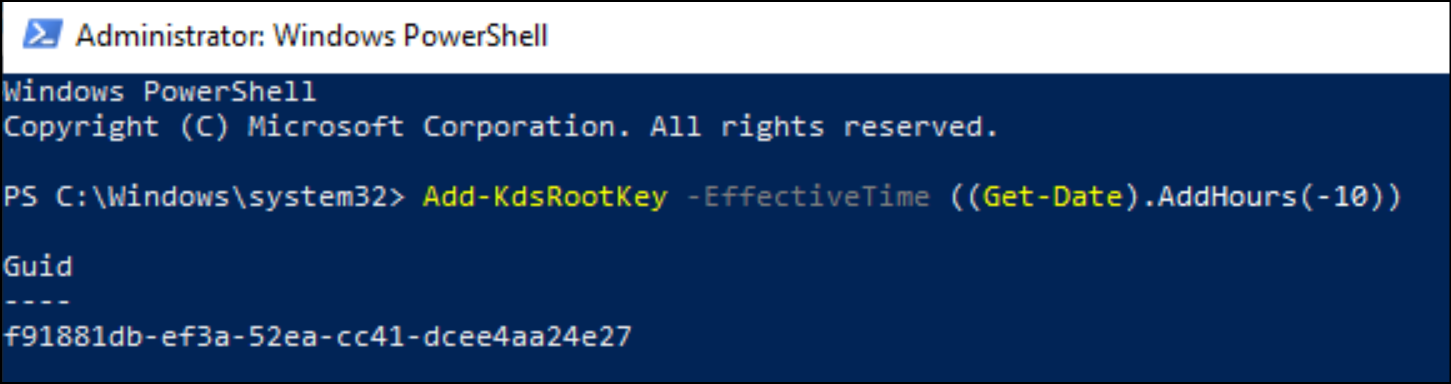
Add-KdsRootKey -EffectiveTime ((Get-Date).AddHours(-10))
The created key is identifiable with a Guid.
The key can be displayed simply by running the command below:
Get-KdsRootKey
This returns a result in this form:
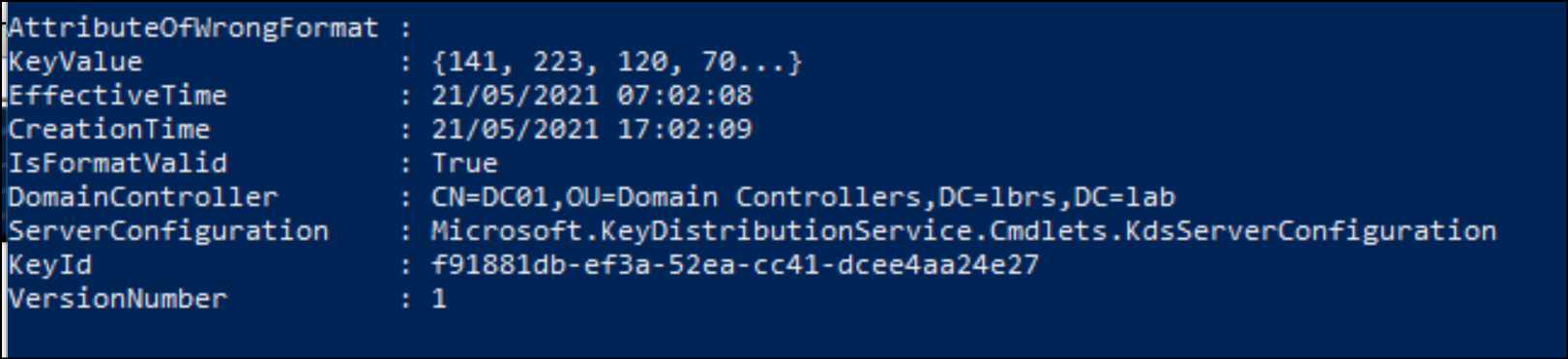
If you want to check the validity of a root key, the Test-KdsRootKey cmdlet can be used. You just have to specify the Guid of the key to check. For example:

If the key is valid, the value true will be returned in the console.
The Kds keys are visible in the “Active Directory Sites and Services” console, by enabling the “Show Services Node” option in the “View” menu.
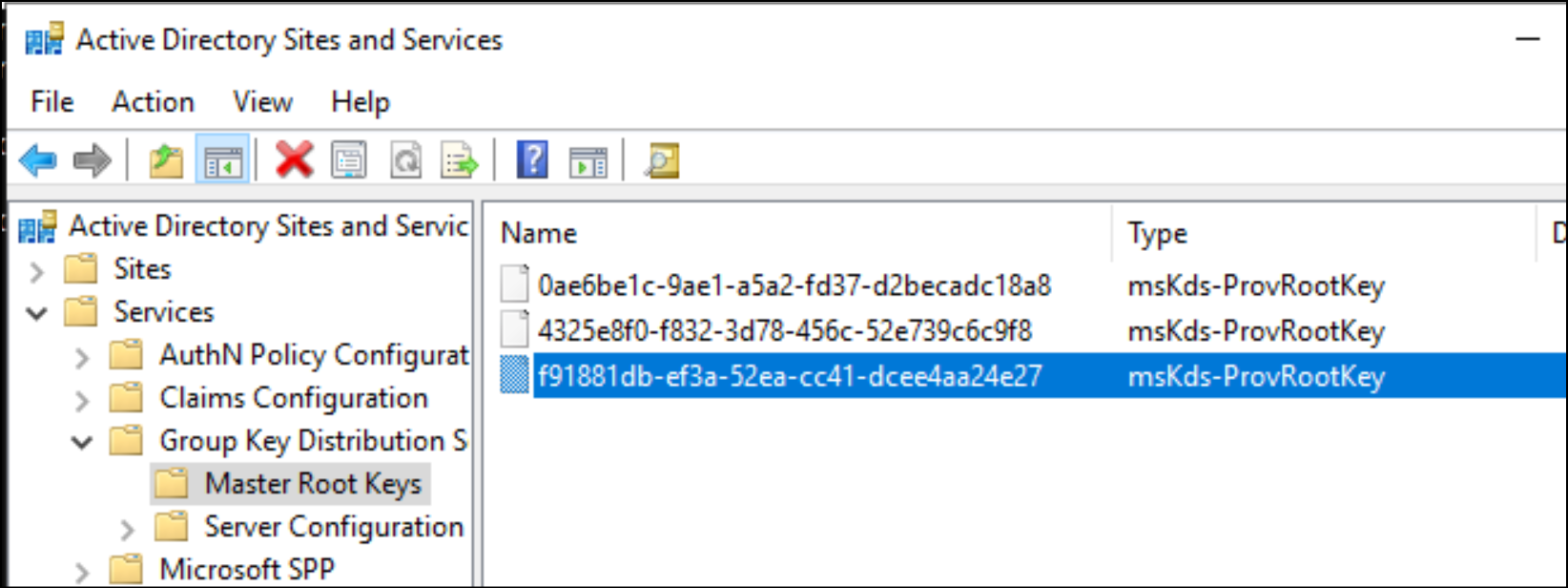
Then browse this way: Services > Group Key Distribution Service > Master Root Keys
create the gMSA account
To create a gMSA on your Active Directory domain, we will use the New-ADServiceAccount cmdlet and different parameters.
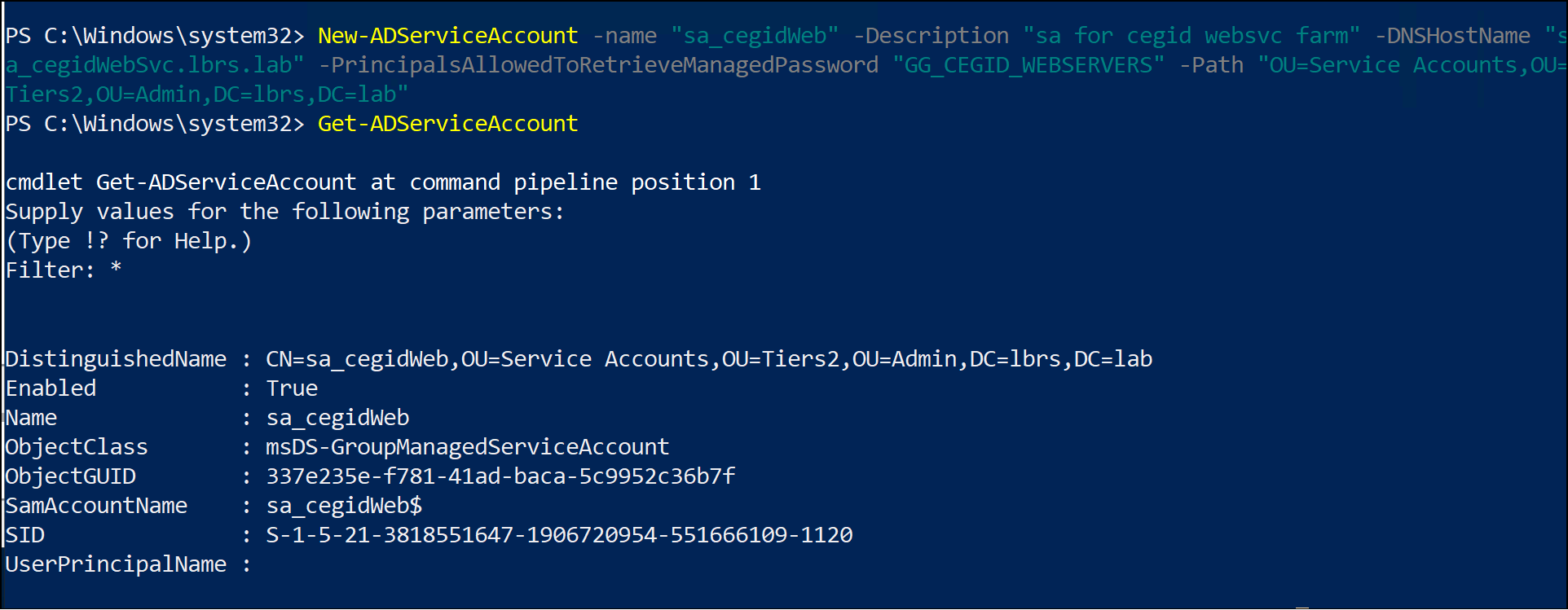
Let’s imagine that we have a farm of Web servers to manage. We have a Global Security Group (GG) than contain all our Web Servers. Here is the command to execute to create and activate a gMSA named “sa_cegidWeb” with a password that renews itself every 30 days.
The computer account “LBRSSRV01$” will be allowed to use this gMSA.
New-ADServiceAccount -Name "sa_cegidWeb"
Description "sa for cegid Web Services Farm"
-DNSHostName "sa_cegidWeb.lbrs.lab"
-ManagedPasswordIntervalInDays 30
-PrincipalsAllowedToRetrieveManagedPassword "GG_CEGID_SERVERS"
-Enabled $True
Some explanations of the parameters:
ManagedPasswordIntervalInDays:
is used to indicate that the password should be reset every X days. This action is automatic and does not require any maintenance action. This attribute is to be defined when creating the gMSA, then it is read only.
PrincipalsAllowedToRetrieveManagedPassword : is used to indicate the object which will be able to use this gMSA and will write the attribute msDS-GroupMSAMembership to the gMSA object. Of course, it is possible to authorize other objects afterwards since a gMSA can be used by several hosts.
DNSHostName: DNS name of this gMSA object
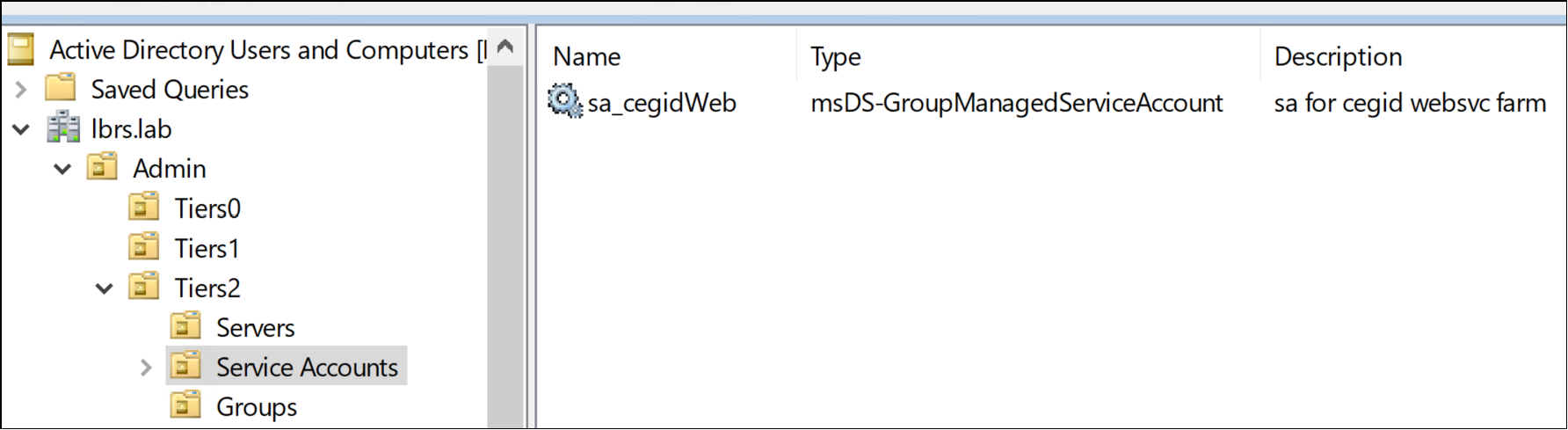
When the gMSA is created, we can find it in the Active Directory within the “Managed Service Account” container by default or in our specified OU:
Add the gMSA to the server
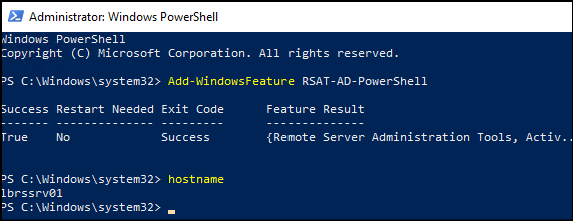
To be used on a server, the gMSA must be installed on this server using a cmdlet that is integrated with the PowerShell module “ActiveDirectory”. (If you are working on a server that is not a domain controller, you must install this module.) This is simply done with the following command:
Add-WindowsFeature RSAT-AD-PowerShell
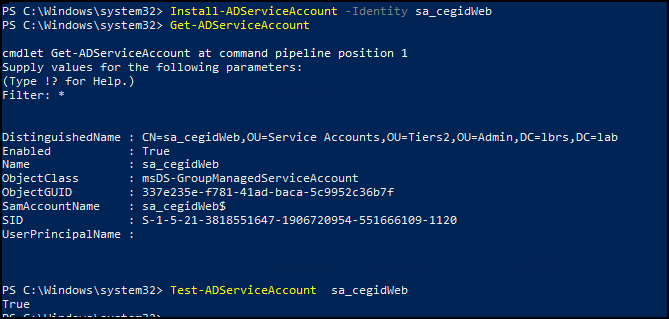
Then we Install the account and we can test it
Install-ADServiceAccount -Identity sa_cegidWeb
Test-ADServiceAccount sa_cegidWeb
Configure The services
Now you can configure your Web service or scheduled tasks with the gMSA Account. remember: AD is the master, if the account is destroyed, the service no longer works.
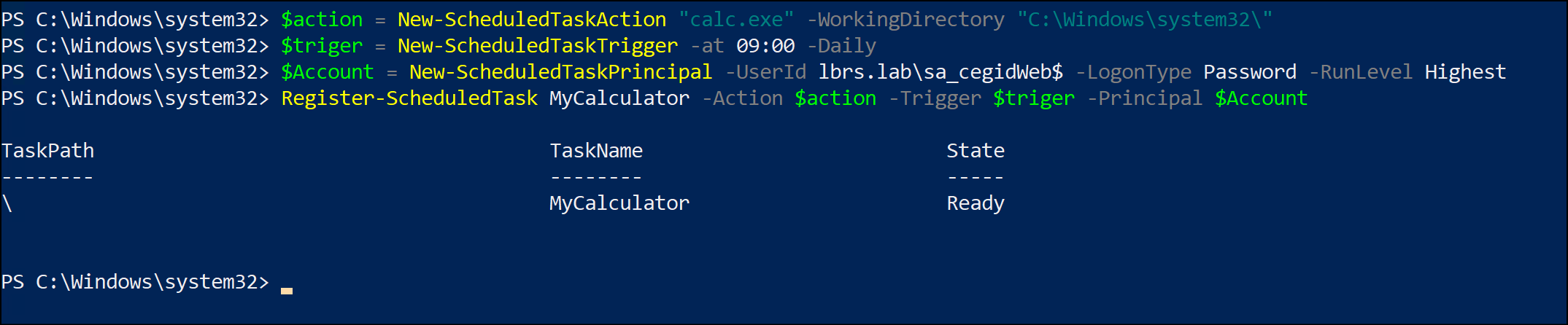
For a Scheduled Task, you’ll need to use Powershell to create the Task:
$action = New-ScheduledTaskAction "calc.exe" -WorkingDirectory "C:\Windows\system32\"
$triger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -at 09:00 -Daily
$Account = New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal -UserId lbrs.lab\sa_cegidWeb$ -LogonType Password -RunLevel Highest
Register-ScheduledTask MyCalculator -Action $action -Trigger $triger -Principal $Account
And you can also use it in the services
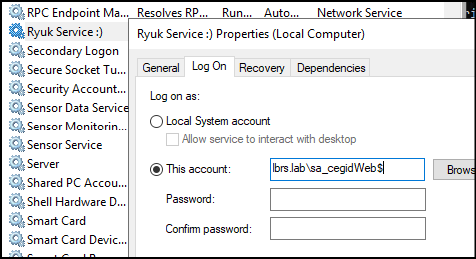
Some will see the little wink on the screenshot 💀
Voilà, you now are ready to deploy gMSA !